ALL ABOUT ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION
Erectile dysfunction (ED) occurs when a man has consistent or repeated problems sustaining an erection. Without treatment, ED can make sexual intercourse difficult. 1 in 5 men report the problem and that number increases with age.
Men who cannot get or maintain an erection that lasts long enough or is hard enough to complete sexual intercourse are considered to have erectile dysfunction, which can be either an occasional problem or a long-term issue.
ED vs. Poor Libido

There are several forms of male sexual dysfunction, including poor libido and problems with ejaculation. But ED refers specifically to problems achieving or maintaining an erection. Men with ED often have a healthy libido, yet the body fails to respond. In many cases, there is a physical basis for the problem. Similarly, men can suffer from poor libido, with or without problems maintaining an erection.
Causes of ED: Chronic Disease
The link between chronic disease and ED is most striking for diabetes. Men who have diabetes are two to three times more likely to have erectile dysfunction than men who do not have diabetes. Among men with erectile dysfunction, those with diabetes may experience the problem as much as 10 to 15 years earlier than men without diabetes. Yet evidence shows that good blood sugar control can minimize this risk. Other conditions that may cause ED include cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), kidney disease, and multiple sclerosis. These illnesses can impair blood flow or nerve impulses throughout the body.
Causes of ED: Lifestyle
Lifestyle choices that impair blood circulation can contribute to ED. Smoking, excessive drinking, and drug abuse may damage the blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the penis. Smoking makes men with atherosclerosis particularly vulnerable to ED. Being overweight and getting too little exercise also contribute to ED. Studies indicate that men who exercise regularly have a lower risk of ED.

Symptoms of ED
The symptoms of ED include:
-
Erections that are too soft for sexual intercourse.
-
Erections that are too brief for sexual intercourse.
-
An inability to achieve erections.
The Mechanics of ED
An erection occurs when blood fills two chambers known as the corpora cavernosa. This causes the penis to expand and stiffen, much like a balloon as it is filled with air. The process is triggered by impulses from the brain and genital nerves. Anything that blocks these impulses or restricts blood flow to the penis can result in ED.
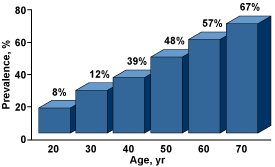
Who Gets ED?
Sexual dysfunction and ED become more common as men age. The percentage of complete ED increases from 5% to 15% as age increases from 40 to 70 years. But this does not mean growing older is the end of your sex life. ED can be treated at any age. Also, ED may be more common in Hispanic and Asian men and in those with a history of diabetes, obesity, smoking, and hypertension. Research shows that African-American men sought medical care for ED twice the rate of other racial groups.
Causes of ED: Surgery
Surgery, including treatments for prostate cancer, bladder cancer, or BPH can sometimes damage nerves and blood vessels near the penis. In some cases, the nerve damage is permanent, and the patient will require treatment to achieve an erection. In others, surgery causes temporary ED that improves on its own after 6 to 18 months.
Causes of ED: Medication
ED may be a side effect of medication, including certain blood pressure drugs, antidepressants, and tranquilizers. Men should talk with their doctor if they suspect a prescription or over-the-counter drug may be causing erectile problems. Never stop any prescribed medicine without first consulting your doctor.

Causes of ED: Psychological
ED usually has something physical behind it, particularly in older men. But psychological factors can be a factor in many cases of ED. Experts says stress, depression, poor self-esteem, and performance anxiety can short-circuit the process that leads to an erection. These factors can also make the problem worse in men whose ED stems from something partly physical.
ED and Bicycling
Research suggests avid cyclists suffer more ED than other athletes. The trouble lies in the shape of some bicycle seats that put pressure on the perineum. This area between the anus and scrotum contains arteries and nerves vital to sexual arousal. Cyclists who ride for many hours each week may benefit from seats designed to protect the perineum.
ED: A Sign of Heart Disease?
In some cases, ED can be a warning sign of more serious disease. One study suggests ED is a strong predictor of heart attack, stroke, and death from cardiovascular disease. The researchers say all men diagnosed with ED should be evaluated for cardiovascular disease. This does not mean every man with ED will develop heart disease, or that every man with heart disease has ED, but patients should be aware of the link.


Treating ED: Lifestyle Changes
Many men with ED are able to improve sexual function by making a few lifestyle changes. Giving up smoking, losing weight, and exercising more often can help by improving blood flow. If you suspect a medication could be contributing to ED, talk to your doctor about adjusting the dosage or switching to another drug.
Treating ED: Prescription Medications
You’ve probably heard of Viagra, but it’s not the only pill for ED. This class of drugs also includes Cialis, Levitra, Staxyn, and Stendra. All work by improving blood flow to the penis during arousal. They're generally taken 30-60 minutes before sexual activity and should not be used more than once a day. Cialis can be taken up to 36 hours before sexual activity and also comes in a lower daily dose. Staxyn dissolves in the mouth. All require a prescription from your doctor for safety.
Treating ED: Alternative Therapies
Herbal supplements for treating ED can contain one or more ingredients that have been traditionally used to remedy male impotence or low libido. Many of the herbal products are popular, even though there may not be a lot of research on their effectiveness. If you have a serious illness, medical condition or you’re taking prescription medications, it’s advisable to consult your doctor or discontinue use of the herbal product if side effects occur as supplements may complicate other health conditions.
ED: Reducing the Risk
Some tips to reduce the risk of ED include:
-
Exercise and maintain a healthy weight
-
Stop smoking
-
Avoid alcohol and substance abuse.
-
Keep diabetes under control

